health
Foods to Eat and Avoid for Optimal Kidney Health
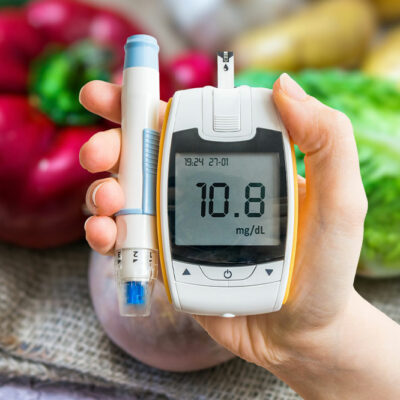
Kidneys help filter waste from the blood and dispose of it off the body via urine. They also help balance the electrolyte and fluid levels in the body. But, conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes may intervene with their ability to work as required. Furthermore, damage to the kidney might also result in chronic kidney disease. Hence making changes in your meal plan is a vital aspect of treatment. You can prevent damage to these organs by following a kidney-healthy meal plan. Below, we will address some foods to eat and avoid for better kidney health. Foods to eat Cauliflower Cauliflower is a nutritious vegetable. It’s an excellent source of folate, Vitamins B, K, and C. It’s rich in anti-inflammatory compounds like indoles, a fiber source. In addition, you can use mashed cauliflower as a replacement for potatoes. For example, a cup of cooked cauliflower has 40 mg of phosphorous, 176 mg of potassium, and 19 mg of sodium. Sweet potatoes They are relatively similar to white potatoes but have more fiber content, resulting in them breaking down more gradually. Hence, you will experience a less spike in insulin levels. Sweet potatoes are also rich in vitamins and minerals like potassium that help balance the sodium levels in the body and lower their impact on the kidneys.
Read More